“ITDP-JDMC partnership has been extremely rewarding in fortifying the initiative towards making Delhi safe for women. The audits at the bus terminals conducted under the guidance of the former have contributed immensely to the understanding of safety issues at the grass root level in cities.”- Ruby Bhardwaj, a member of faculty at Janki Devi Memorial College (JDMC)
Written by Sonal Shah
Transport – be it streets, buses, metro-rail, rickshaws – is not only infrastructure that we use for daily movement, but also constitutes our image of the city and how accessible or inaccessible it is – depending on our social identity.
To explore the intersections of Gender and Transport, in October 2017, ITDP co-taught a course on ‘Safe and Inclusive Cities’ at the Janki Devi Memorial College (or JDMC). Under the ‘Urban Planning and Infrastructure’ module, ITDP highlighted the dimensions of gendered travel such as trip chaining, forced mobility, forced immobility, and mobility of care. Trip-chaining and the mobility of care look at women’s travel patterns, as they make multiple stops on their way to a destination for caretaking trips (such as accompanying a dependant to school, clinics, shopping for the household etc). Forced immobility is a consequence of violence and insecurity in transport, which constrains their movement. Introducing these concepts to enabled the young women of JDMC college to evaluate their daily paths through the lens of walkability, safety and comfort.
As a part of the course, the students walked as a group and mapped the street from JDMC to Karolbagh Metro Station, the residential streets in the vicinity and Gangaram Hospital Road. They highlighted how encroached, discontinuous and inadequate footpaths forced them to walk on the carriageway, how high boundary walls along deserted stretches became places where men urinated, how ‘dark spots’ due to poor street lighting and inactive stretches increased unsafe walking conditions, how drinking tea at a vendor was uncomfortable because they were “looked” at by male bystanders or how they altered their walking path to take a longer route or avoid an unsafe stretch.
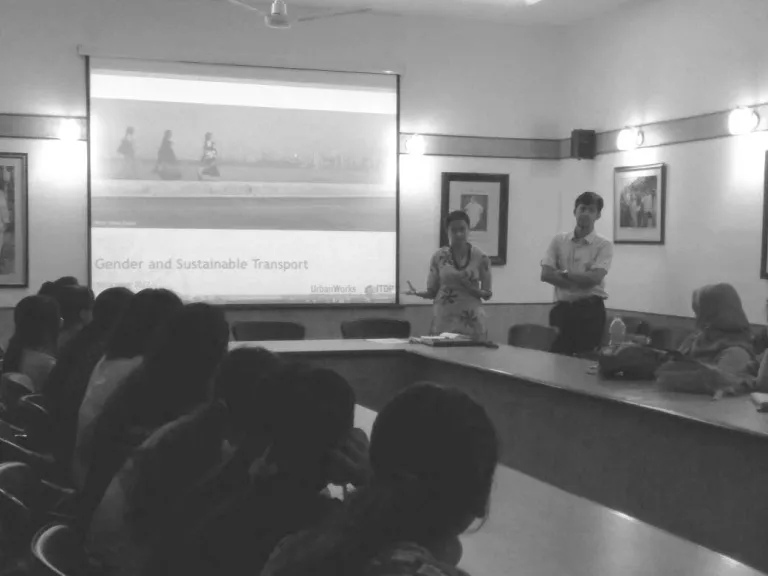

ITDP staff presenting the intersections of Gender and Transport
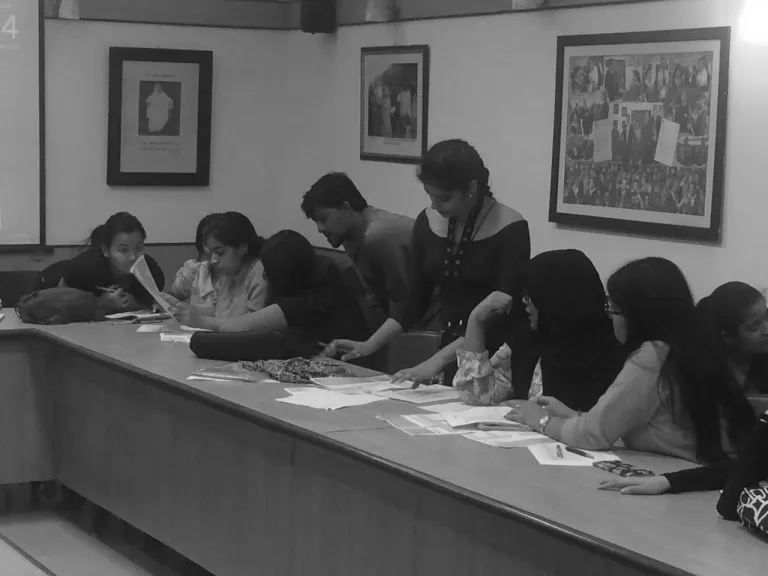

ITDP staff discussing the mapping exercise and proposals on how streets could be made safer with JDMC students
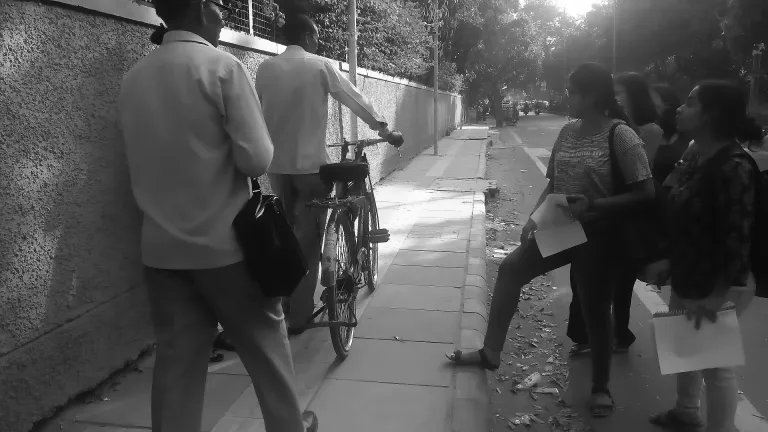
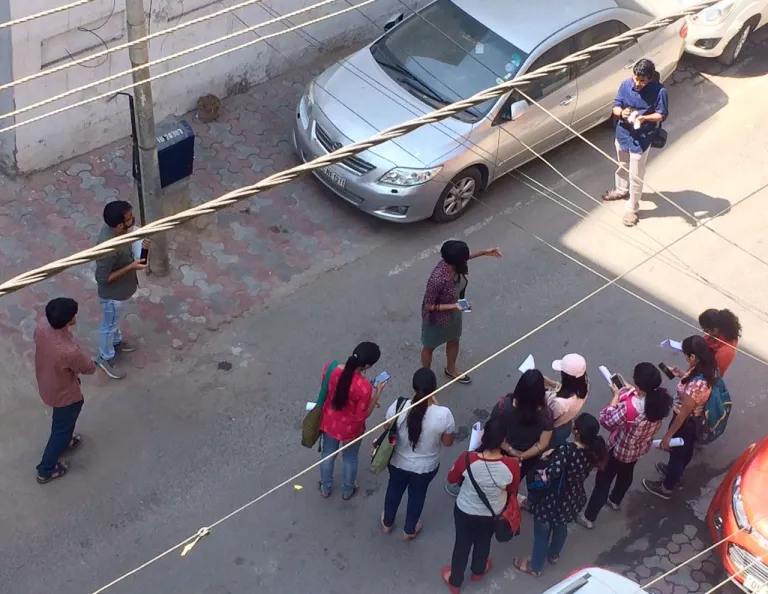
This short exercise has been followed by a second workshop in March 2018, where the same students are now conducting walkability assessments and safety audits using the Safetipin application within 500m around bus terminals in Delhi. This will culminate in a report rating the quality of walking infrastructure and the built environment and suggest concrete recommendations for creating gender responsive streets. Sonali Vyas from Safetipin conducted a training session on how to use the application, followed by pilot test audits.
Our preliminary findings reveal that road safety, quality of walking infrastructure, street lighting, gender diversity are consistently emerging as issues in accessing the bus terminals across Delhi. While the comprehensive findings will be shared in April, this exercise reflects ITDP’s endeavour to engage students (in this case, young sociology female students) in not only understanding gendered transport theoretically, but becoming aware of how accessibility can be enabled or hindered and the critical role that infrastructure plays in it.
JDMC students mapping the streets around their college.

We would like to acknowledge the students and faculty of Janki Devi Memorial College and Safetipin in this joint initiative.
Right: ITDP staff explaining how to conduct a safety audit on the field.
