Written by C. Ranga Rohini, ITDP
With a population of over 4.7 million and with a rapidly growing economy, the city of Chennai faces the challenge of providing efficient, safe, and reliable transport solutions to its citizens without compromising on quality of life. The onus of this responsibility currently falls on a number of agencies in the city and brings with it a slew of issues in planning, coordination, and accountability. The Chennai Unified Metropolitan Transport Authority (CUMTA) was formed in November 2010 with the aim to address these issues—to serve as a single nodal agency that directs planning, operations, and monitoring of various transport modes in the metropolitan area of Chennai. One of CUMTA’s key responsibilities is the preparation of a Comprehensive Transport Plan that looks at the planning and development of public transport options and their implementation through various agencies.
Written by C. Ranga Rohini, ITDP
To facilitate this process, CMDA, in collaboration with the Institute of Transport and Development Policy, organized a workshop from 22 to 24 January 2013 that brought together various government stakeholders along with experts and academicians to discuss the CUMTA’s vision and to develop viable strategies and actions to carry the vision forward.
In this video, Pranjal Kulkarni—Senior Research Associate, Urban Development at the ITDP India Programme—takes you through Pune’s journey of ensuring safe, affordable, and sustainable transport with a showcase of the city’s achievements in non-motorised and public transport, and exclusive interviews with the city’s officials who have enabled the city’s dramatic transformation.
Participants formed groups to deliberate on four primary topic areas: 1) CUMTA as an agent of change for the Chennai Metropolitan Area: defining CUMTA’s role as a planning, monitoring, and coordinating body to facilitate interagency coordination. 2) Developing an integrated, high quality bus and BRT network for the entire city: expanding the bus fleet, implementing BRT, introducing an integrated fare collection systems across modes, and providing customer information. 3) Improving streets and the public realm: developing pedestrian friendly street design standards and planning guidelines, identifying greenway networks, and improving intermodal links. 4) Management of road space and travel demand: implementing a robust on-street parking management system, facilitating compact development around public transport stations, and implementing dynamic road pricing solutions.
At the workshop, Mr. Ben Plowden, Director of Surface Transport at Transport for London, described the city of London’s experience in bringing multiple public transport providers under a single umbrella, starting in 2000. He showed how London has been able to achieve a reduction in the use of private cars over the past decade through the steady expansion of sustainable transport options, including expanded bus service and a network of high quality cycle tracks. “You need a transport system that is adequate to meet the demands that the city will put on it,” pointed out Mr. Plowden. “That means focusing on mass transit.”
Workshop attendees included representatives from CMDA, the Corporation of Chennai, Chennai Metro Rail Limited, Highways Department, Transport Department, TNRDC, Metropolitan Transport Corporation, consultants, NGO Chennai City Connect, faculty from the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, School of Architecture and Planning, Anna University, and representatives from unified metropolitan transport authorities in Bangalore and Delhi, among others.
To achieve the vision of transforming Chennai into a world-class city, a general consensus was reached on the need to assess existing resources, identify short-term goals, and focus on early wins to build CUMTA’s reputation. Participants stressed the role of data collection in enabling evidence-based planning and identified a need for a financial audit of existing spending patterns. “Data collection is critical,” explained Mr. K. Phanindra Reddy, Secretary of the Department of Housing and Urban Development, Government of Tamil Nadu. “Unless we know the scenario we are starting with, and the lacunae that we need to address, we will be groping in the dark.”
A key initiative to emerge in the workshop’s action plan is the creation of a common information portal for all public transport modes in Chennai. Geographically focused, time-bound pilot projects on pedestrianization, parking, street design, and multi-modal integration were also identified. ITDP has begun compiling the outcomes of the workshop into a strategic plan to be adopted by CUMTA. “The stakeholders have come out with each and every suggestion,” said Mr. Reddy. “That is a critical element for success of CUMTA. It’s time that we turn our plans into assets on the street.”
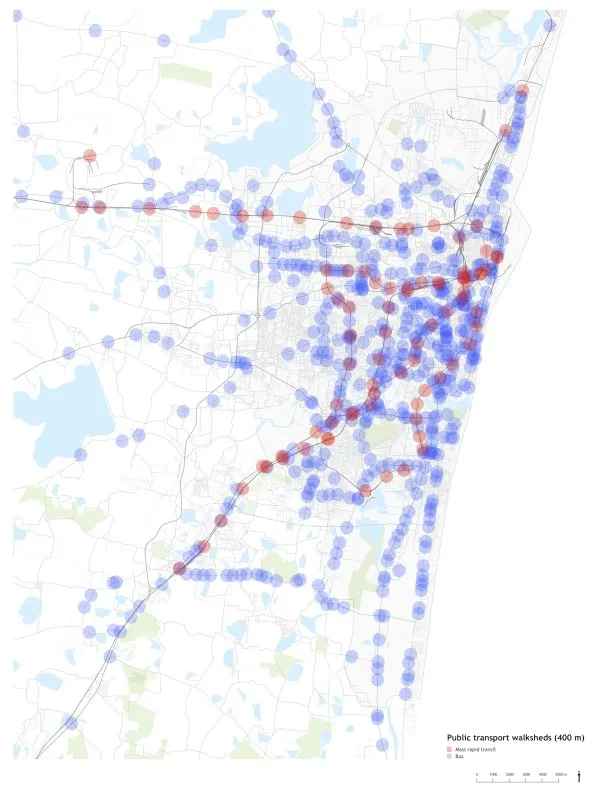
Ensuring that all Chennai residents have access to high quality public transport was a key theme during the workshop. Shown above are the areas within a 5 minute walk of public transport.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
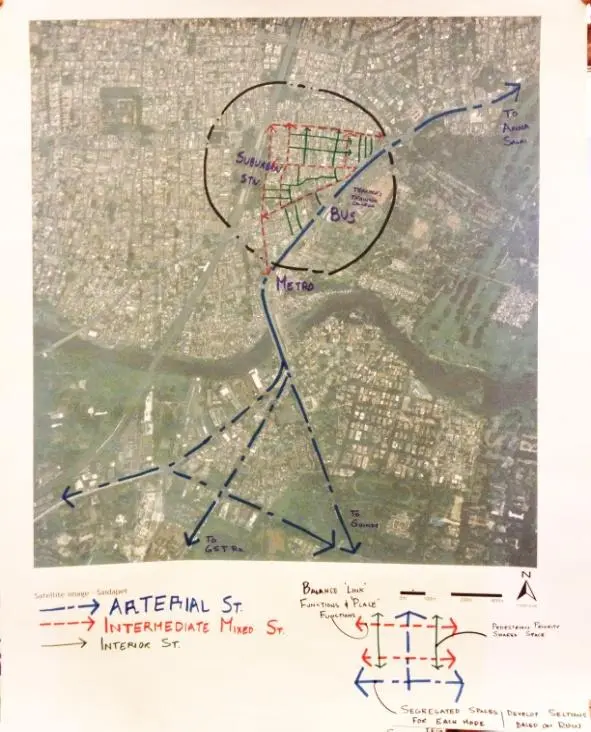
Participants discussed the importance of balancing the “link” and “place” functions of streets, using Chennai’s Saidapet area as a case study.
